You can usually ignite a compressed fuel/air mixture through a spark plug, but do you really understand the thermal range of a spark plug? To make things easier and help you understand this basic term, we now introduce you to the definition of spark plug heat range and how it affects your engine and how to use it properly.
First of all, let’s give a clear explanation of the heat path of a spark plug.
A Guide to Spark Plug Heat Range: What is Spark Plug Heat Range?
The spark plug heat range is the speed at which the spark plug can transfer heat from the ignition tip to the cylinder head, water jacket, and cooling system. The thermal range of a spark plug varies from spark plug to spark plug and can be recorded in a number of different ways, which makes it quite difficult to compare brands from brand to brand.

The spark plug heat path is the speed at which the spark plug can transfer heat from the ignition tip to the cylinder head, water jacket, and cooling system. Source: Lesserman
Car Spark Plug Tutorial: Specifically, if the spark plug overheats, your engine may experience knocking, early ignition, or loss of power. If the spark plug is too cold, it will not be able to self-clean properly by burning off the carbon deposits. Therefore, choosing the right heating range is essential for a high-performance engine.
Generally, spark plug manufacturers recommend that tip temperatures be kept around 500 – 850 degrees Celsius. The heat range numbering system used by spark plug manufacturers is not universal. Some manufacturers have the opposite numbering system for the other – for Champion, Autolite, and Bosch, the higher the number, the hotter the plug. However, for NGK, the higher the number, the colder the plug.
What is a spark plug? What is a Cold Spark Plug?
Each spark plug manufacturer designs a number for the heat stroke. Typically NGK spark plugs have a heating range between 2-11. Broadly speaking, spark plugs are often referred to as hot or cold spark plugs.
Spark plugs
A spark plug is a plug that slowly transfers heat from the ignition tip to the head of the engine, keeping the ignition tip at a higher temperature. Knocking (engine knocking) or central electrode breakdown is a symptom of overheating of the spark plug. Hot-swappable is suitable for applications that operate primarily at low speeds. Since they have a longer insulator nose length, heat is transferred from the ignition tip to the cooling system at a slower rate.
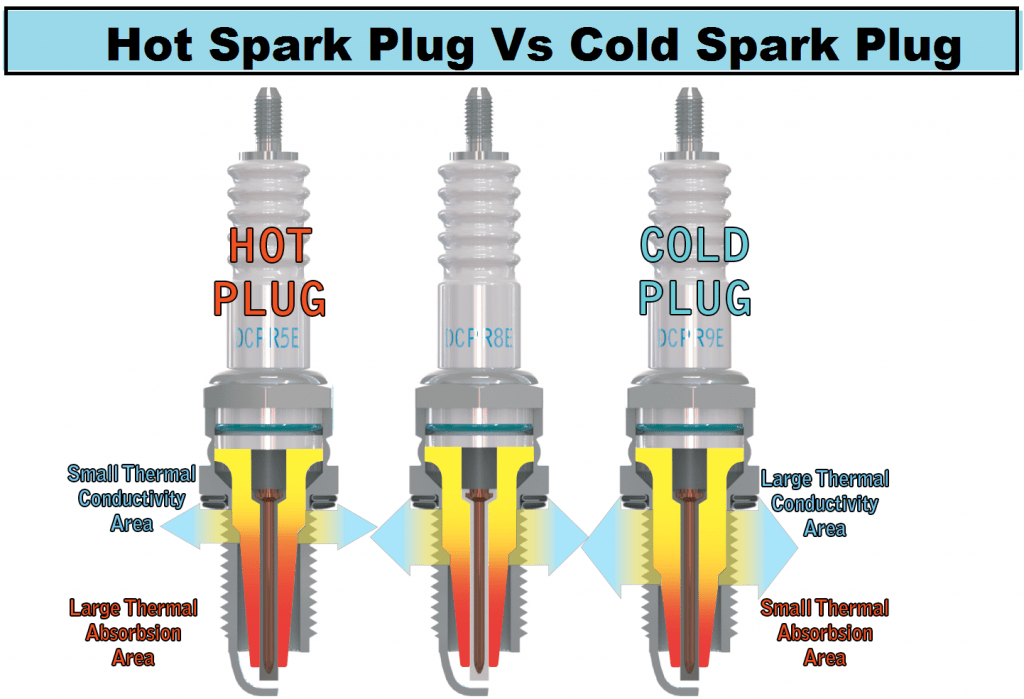
Hot and cold spark plugs
Cold spark plugs
A cold spark plug is a type of spark plug that conducts more heat from the tip of the spark plug and lowers the temperature of the tip. Cold plugs are ideal for high-rpm engines, forced-air intake applications, and other situations where engines generate high operating temperatures. Whether a spark plug is hot or cold is known as the hot range of the spark plug.
What happens if the heating range is too high or too low?
A guide to the heat range of the spark plug: The heating range is too high
Although not as damaging as plugs with an underrated rating, the effects can still be detrimental to your engine. If the temperature of the spark plug is still too low, there is a risk that the ignition spark will be lost due to deposit buildup at the ignition end, which in turn will put your engine in a bind/power drop.
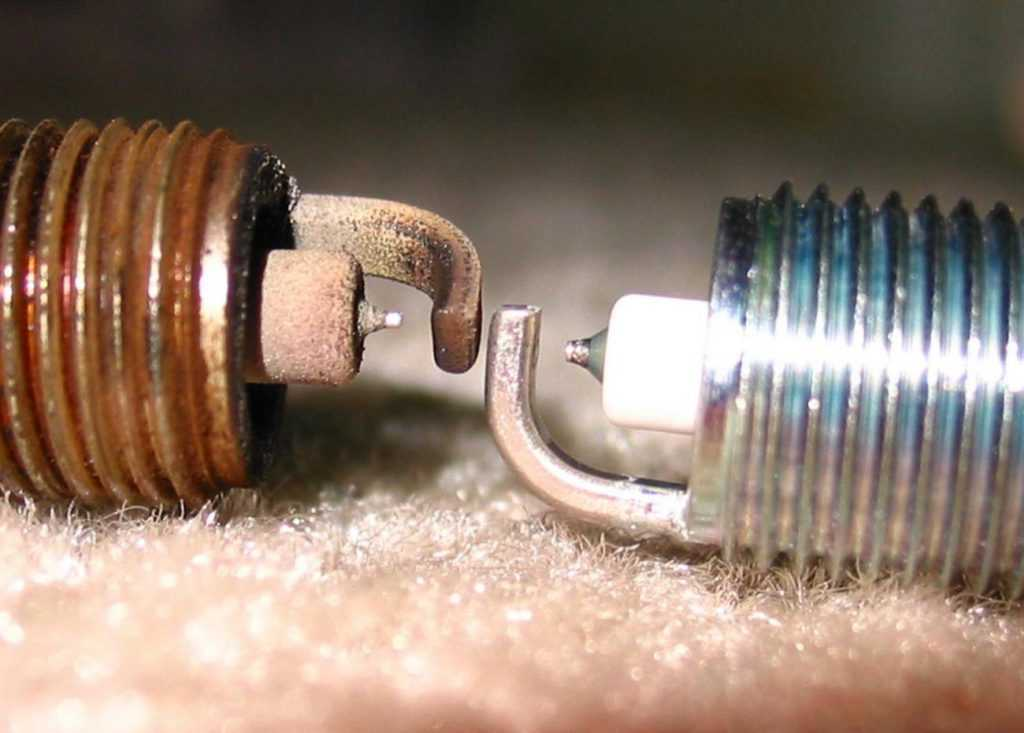

If the temperature of the spark plug is kept too low, there is a risk that the ignition spark will be lost due to the build-up of deposits at the ignition end, which in turn will make your engine struggle and power drop. Source: Autoportal.com
Car spark plug tutorial: The heating range is too low
When the heat range is too low, it can cause a lot of damage to your vehicle’s engine because the spark plug can overheat and cause abnormal ignition (early ignition), which can cause the spark plug electrodes to melt and the piston to get stuck and corroded.
Brief description of the rules:
Low-power engines – low heat range or spark plugs
High-power engines – high hot range or cold spark plugs
Thermal range reference diagram
As we mentioned above, NGK spark plugs have a heating range ranging from 2-11. Let’s take a look at the heat range chart with complete information about that number. You will have a basic understanding of the hot and cold spark plugs of the 5 major spark plug brands.
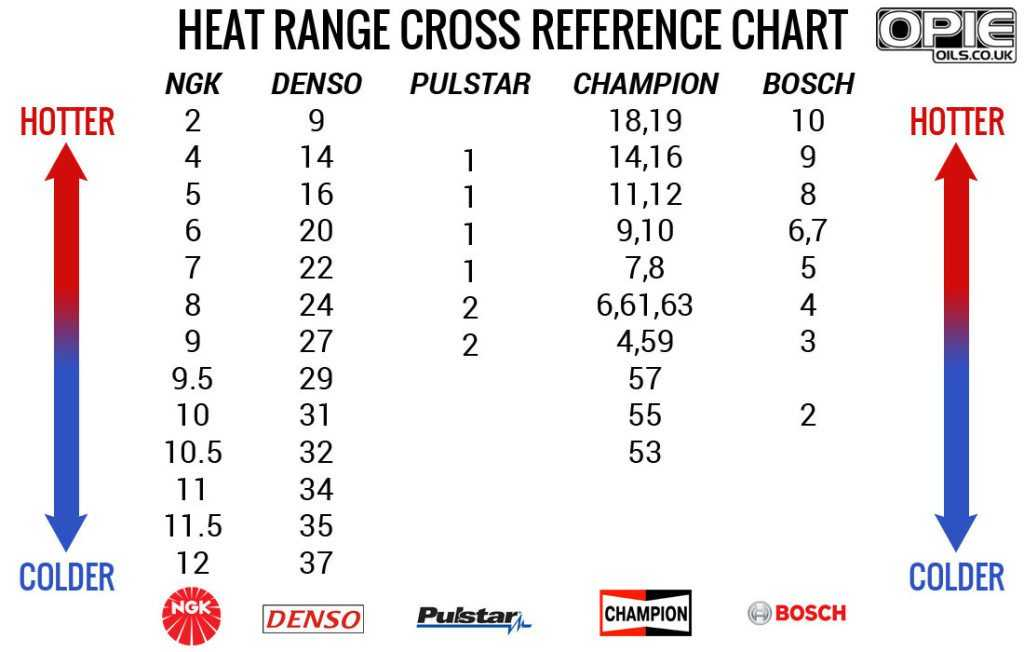
Having to replace a new spark plug is a pain, but you absolutely need to know what kind of hot or cold spark you need and at what rate. So every time you’re wondering “what kind of heat range spark plug should I use”, take a look at this chart and you’ll understand!
A Guide to Spark Plug Heat Ranges: Basic Heat Ranges
Nitrous oxide
Nitrous oxide is a factor that causes high cylinder temperatures. Therefore, it needs to have a colder heating range on the stock plug.
Methanol
Metanon is believed to have a higher octane rating than standard gasoline, and methanol provides a more complete combustion. In that case, you may need a cooler plug to transfer more heat from the combustion chamber.
Air/fuel mixture modifications
The lean air/fuel mixture can increase the operating temperature as well as the tip temperature, which can lead to knocking or early ignition. For thinner air/fuel mixtures, you should use a cooler heat range. Since the concentrated air/fuel mixture can cause the spool temperature to drop, which can lead to carbon build-up on the tip, you should use a hotter heating range for the concentrated air/fuel mixture.
Long acceleration/high speeds
Frequent and prolonged acceleration and high-rpm driving can increase the combustion temperature, often requiring a colder heating range.
Ignition timing in advance
In general, early ignition timing increases the spark plug temperature. In fact, NGK estimates that the ignition timing increases by 70° to 100° for every 10° advance. Therefore, you may need to use a cooler heating range to avoid knocking or early ignition.
Automotive Spark Plug Tutorial: Improving the Compression Ratio
A higher compression ratio means higher cylinder pressure and temperature. Similarly, you may need a cooler range of heat to quickly transfer all the extra heat to the cooling system.
Supercharged/turbocharged
Pressurized forced sensing causes an increase in cylinder pressure and temperature, which can lead to knocking. Depending on the application, you may need to use a significantly colder hot range backlog.
Summary of guidelines for spark plug heat ranges
Make yourself aware of the thermal range of the spark plug before replacing it, this will help you avoid any serious damage to your car. Don’t forget to follow our maintenance tips to get to know your car better and learn how to fix it if needed.